Amitriptyline is a first-line remedy for migraine prevention and treatment, the only one among antidepressants that has proven effectiveness of such use. The results of a placebo-controlled study indicate that the use of amitriptyline (50-100 mg per day) for four weeks in 50% of patients helps to reduce the migraine index on average by a factor of 0.62 (migraine index is an indicator that includes the frequency and duration of seizures ).
In the comparative studies of amitriptyline and propranolol, propranolol was found to be more effective in patients with monotypic migraine, and amitriptyline in mixed migraine and stress symptoms. Amitriptyline is also well established with concomitant insomnia or depression (in the latter case, high doses of the drug are needed).
Side effects of amitriptyline – dizziness, weight gain, anticholinergic symptoms (dry mouth). Amitriptyline is tolerated by patients somewhat worse than some other tricyclic antidepressants (for example, nortriptyline, doxepin), and their analgesic effect in cases of pain not of migraine origin is the same.
Therefore, in individuals who can not take amitriptyline because of the expressed indirect effect, you can try to use other tricyclic antidepressants. However, this approach is not proven, as there is much evidence that other tricyclic antidepressants (other than amitriptyline) are unsuitable for the prevention of migraine, as well as selective inhibitors of serotonin reuptake.
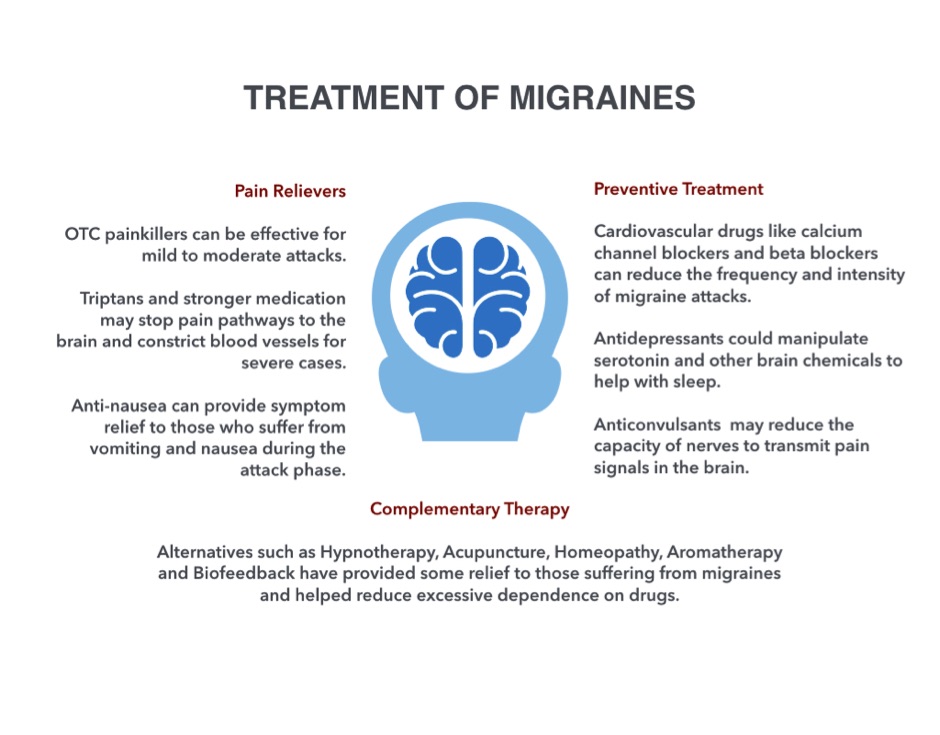
Anticonvulsants for migraine
Valproic acid and its derivatives. Divalprox and sodium valproate are medications with proven efficacy for the prevention of migraine. With a 50% reduction in the frequency of seizures, the sodium valproate efficacy ratio was 3.1, and for the diwalprox, 4.8. However, anticonvulsant drugs are considered drugs with a high level of toxicity, so the question of the benefit/risk ratio and monitoring of possible intoxication should be carefully investigated.
Side effects – nausea, fatigue, tremor, weight gain, dizziness, gastrointestinal disorders (read diarrhea than to treat) – decrease with prolonged use of anticonvulsants. These funds for migraine are contraindicated in chronic pancreatitis or hepatitis, liver cirrhosis. They have a teratogenic effect and can not be used in pregnant women.
Gabapentin. According to two studies, gabapentin is effective at a dose of 1200-2400 mg/day, this dosage reduces the frequency of migraine attacks by a factor of two. The most common side effects are dizziness and drowsiness.
Topiramate. The effectiveness of this remedy for migraine has been proven in many studies, which makes it a first-line preparation for the prevention of migraine. Topiramate manifests effects after a month of use, after 26 weeks at a dose of 50 mg/day, it facilitated migraine relief in 36% of cases, and at a dose of 200 mg/day – in 52%. The toxicity index of the drug is high enough. The severity of side effects (paresthesia, fatigue, nausea and anorexia) increases with increasing dose.
The effectiveness of other means for migraine prevention is still at the study stage.
 English(UK)
English(UK) Nederlands
Nederlands